RocksDB Iterator Internal, part 3
RocksDB Iterator系列的最后一篇,看一看SST文件的格式,以及基于SST的迭代器是如何工作的。
BlockBasedTableIterator
我们之前在第一篇介绍过,一个SST文件的LevelIterator是经过下面的路径,最终被加入到DBIter中的。
DBImpl::NewIterator
-> DBImpl::NewIteratorImpl
-> DBImpl::NewInternalIterator
-> Version::AddIterators
-> Version::AddIteratorsForLevel
-> new LevelIterator
而LevelIterator更像一个wrapper,对于任何一个SST文件,它会检查这个文件是否已经被打开,对应的数据是否在BlockCache中等等,而最核心部分的功能是由BlockBasedTableIterator完成的。从LevelIterator::Seek相关代码就能看到:
- 首先在
TableCache这一层会尝试打开SST文件,如果之前已经打开了对应文件,则直接使用之前的句柄 - 如果之前没有打开这个SST文件,生成对应的TableReader,加入到
TableCache中 - 由于
BlockedBaseTable中有index block和data block,因此需要把IndexBlockIterator也生成,并传入到BlockBasedTableIterator中 - 最终调用
BlockBasedTableIterator::Seek
LevelIterator::Seek
-> LevelIterator::InitFileIterator
-> LevelIterator::NewFileIterator
-> TableCache::NewIterator
-> BlockBasedTable::NewIterator
-> new BlockBasedTableIterator
-> BlockBasedTableIterator::Seek
InternalIterator* BlockBasedTable::NewIterator(
const ReadOptions& read_options, const SliceTransform* prefix_extractor,
Arena* arena, bool skip_filters, TableReaderCaller caller,
size_t compaction_readahead_size, bool allow_unprepared_value) {
BlockCacheLookupContext lookup_context{caller};
bool need_upper_bound_check =
read_options.auto_prefix_mode || PrefixExtractorChanged(prefix_extractor);
std::unique_ptr<InternalIteratorBase<IndexValue>> index_iter(NewIndexIterator(
read_options,
/*disable_prefix_seek=*/need_upper_bound_check &&
rep_->index_type == BlockBasedTableOptions::kHashSearch,
/*input_iter=*/nullptr, /*get_context=*/nullptr, &lookup_context));
if (arena == nullptr) {
return new BlockBasedTableIterator(
this, read_options, rep_->internal_comparator, std::move(index_iter),
!skip_filters && !read_options.total_order_seek &&
prefix_extractor != nullptr,
need_upper_bound_check, prefix_extractor, caller,
compaction_readahead_size, allow_unprepared_value);
} else {
auto* mem = arena->AllocateAligned(sizeof(BlockBasedTableIterator));
return new (mem) BlockBasedTableIterator(
this, read_options, rep_->internal_comparator, std::move(index_iter),
!skip_filters && !read_options.total_order_seek &&
prefix_extractor != nullptr,
need_upper_bound_check, prefix_extractor, caller,
compaction_readahead_size, allow_unprepared_value);
}
}
注意
BlockBasedTableIterator构造的第5个参数如果为true,即没有指定total_order_seek且指定了prefix_extractor时,可以在使用BlockBasedTableIterator时通过检查前缀布隆过滤器是否匹配,避免读取index block和data block。
Index
目前RocksDB有三种索引类型:
BinarySearchIndex: 最常见的形式,二分查找。HashIndex: 哈希索引,如果同时配置了prefix_extractor时,会通过哈希进行查找。如果用户在读取时指定ReadOptions.total_order_seek = true,就可以忽略索引,直接查找data block。PartitionIndex: 当数据量特别大时,默认的index/filter都不计入在BlockCache容量之内,而index/filter又会保存在内存中。而PartitionIndexReader就会将index分层,通过配置可以只将top level index放在内存中,减少内存消耗。
BinarySearchIndex和PartitionIndex保证有序,HashIndex在默认total_order_seek为false的情况下无法保证有序
以默认的BinarySearchIndex为例,看下是如何读取构造index block的reader路径的。在构造BlockBasedTableIterator之前,会先调用NewIndexIterator。调用路径如下:
BlockBasedTable::NewIterator
-> BlockBasedTable::NewIndexIterator
-> BinarySearchIndexReader::NewIterator
or HashIndexReader::NewIterator
or PartitionIndexReader::NewIterator
-> Block::NewIndexIterator
-> IndexBlockIter::Initialize
// disable_prefix_seek should be set to true when prefix_extractor found in SST
// differs from the one in mutable_cf_options and index type is HashBasedIndex
InternalIteratorBase<IndexValue>* BlockBasedTable::NewIndexIterator(
const ReadOptions& read_options, bool disable_prefix_seek,
IndexBlockIter* input_iter, GetContext* get_context,
BlockCacheLookupContext* lookup_context) const {
assert(rep_ != nullptr);
assert(rep_->index_reader != nullptr);
// We don't return pinned data from index blocks, so no need
// to set `block_contents_pinned`.
return rep_->index_reader->NewIterator(read_options, disable_prefix_seek,
input_iter, get_context,
lookup_context);
}
disable_prefix_seek只是提供给HashIndex使用(比如当prefix_extractor发生变化时,HashIndex就不能使用SST中之前生成的索引,此时需要禁用),其他两种索引后续都会忽略这个参数。
以BinarySearchIndex为例,注意它调用NewIndexIterator的第5个参数true对应total_order_seek。
InternalIteratorBase<IndexValue>* BinarySearchIndexReader::NewIterator(
const ReadOptions& read_options, bool /* disable_prefix_seek */,
IndexBlockIter* iter, GetContext* get_context,
BlockCacheLookupContext* lookup_context) {
const BlockBasedTable::Rep* rep = table()->get_rep();
const bool no_io = (read_options.read_tier == kBlockCacheTier);
CachableEntry<Block> index_block;
const Status s =
GetOrReadIndexBlock(no_io, read_options.rate_limiter_priority,
get_context, lookup_context, &index_block);
if (!s.ok()) {
if (iter != nullptr) {
iter->Invalidate(s);
return iter;
}
return NewErrorInternalIterator<IndexValue>(s);
}
Statistics* kNullStats = nullptr;
// We don't return pinned data from index blocks, so no need
// to set `block_contents_pinned`.
auto it = index_block.GetValue()->NewIndexIterator(
internal_comparator()->user_comparator(),
rep->get_global_seqno(BlockType::kIndex), iter, kNullStats, true,
index_has_first_key(), index_key_includes_seq(), index_value_is_full());
assert(it != nullptr);
index_block.TransferTo(it);
return it;
}
构造和初始化IndexBlockIter的相关代码,所有类型的索引都会调用到Block::NewIndexIterator。
IndexBlockIter* Block::NewIndexIterator(
const Comparator* raw_ucmp, SequenceNumber global_seqno,
IndexBlockIter* iter, Statistics* /*stats*/, bool total_order_seek,
bool have_first_key, bool key_includes_seq, bool value_is_full,
bool block_contents_pinned, BlockPrefixIndex* prefix_index) {
IndexBlockIter* ret_iter;
if (iter != nullptr) {
ret_iter = iter;
} else {
ret_iter = new IndexBlockIter;
}
if (size_ < 2 * sizeof(uint32_t)) {
ret_iter->Invalidate(Status::Corruption("bad block contents"));
return ret_iter;
}
if (num_restarts_ == 0) {
// Empty block.
ret_iter->Invalidate(Status::OK());
return ret_iter;
} else {
BlockPrefixIndex* prefix_index_ptr =
total_order_seek ? nullptr : prefix_index;
ret_iter->Initialize(raw_ucmp, data_, restart_offset_, num_restarts_,
global_seqno, prefix_index_ptr, have_first_key,
key_includes_seq, value_is_full,
block_contents_pinned);
}
return ret_iter;
}
Seek
BlockBasedTableIterator::Seek的实现如下,我们只保留主干路径:
- 如果条件允许,检查prefix bloom filter是否匹配,如果不匹配可以直接返回无效迭代器,跳过后续的IO操作
- 用索引进行Seek,不同索引类型对应不同read,如
BinarySearchIndexReader、HashIndexReader、PartitionIndexReader,最常见的BinarySearchIndex最终会调用IndexBlockIter::Seek - 根据索引查找结果,决定是否要读取data block
void BlockBasedTableIterator::SeekImpl(const Slice* target,
bool async_prefetch) {
// ...
// 如果可以用前缀匹配进行判断,且前缀的确不匹配,可以将Iterator置为无效,并直接返回
if (target && !CheckPrefixMayMatch(*target, IterDirection::kForward)) {
ResetDataIter();
return;
}
bool need_seek_index = true;
// ...
// 一些情况下need_seek_index可以设置为false
if (need_seek_index) {
if (target) {
index_iter_->Seek(*target);
} else {
index_iter_->SeekToFirst();
}
if (!index_iter_->Valid()) {
ResetDataIter();
return;
}
}
IndexValue v = index_iter_->value();
const bool same_block = block_iter_points_to_real_block_ &&
v.handle.offset() == prev_block_offset_;
if (...) {
// ...
// 一些情况下,根据索引查找结果就不需要再读取data block
ResetDataIter();
} else {
// Need to use the data block.
if (!same_block) {
if (read_options_.async_io && async_prefetch) {
// ...
// async io优化
} else {
// 初始化data block
InitDataBlock();
}
} else {
// ...
CheckDataBlockWithinUpperBound();
}
// 读取data block
if (target) {
block_iter_.Seek(*target);
} else {
block_iter_.SeekToFirst();
}
FindKeyForward();
}
CheckOutOfBound();
if (target) {
assert(!Valid() || icomp_.Compare(*target, key()) <= 0);
}
}
- 前缀布隆过滤器匹配
check_filter_就是指是否要检查prefix bloom filter匹配,即BlockBasedTable::NewIterator构造的第五个参数,当total_order_seek为true且prefix_extractor不为空时,就可以通过SST文件中的前缀布隆过滤器进行检查。
bool CheckPrefixMayMatch(const Slice& ikey, IterDirection direction) {
if (need_upper_bound_check_ && direction == IterDirection::kBackward) {
// Upper bound check isn't sufficient for backward direction to
// guarantee the same result as total order, so disable prefix
// check.
return true;
}
if (check_filter_ && !table_->PrefixRangeMayMatch(
ikey, read_options_, prefix_extractor_,
need_upper_bound_check_, &lookup_context_)) {
// TODO remember the iterator is invalidated because of prefix
// match. This can avoid the upper level file iterator to falsely
// believe the position is the end of the SST file and move to
// the first key of the next file.
ResetDataIter();
return false;
}
return true;
}
相关代码很多,这里只把调用逻辑列出:
BlockBasedTable::PrefixRangeMayMatch
-> FilterBlockReaderCommon<TBlocklike>::RangeMayExist
-> FullFilterBlockReader::PrefixMayMatch
-> FullFilterBlockReader::MayMatch
-> FastLocalBloomBitsReader::MayMatch
- 读取index block,实际就是对index block进行二分查找
void IndexBlockIter::SeekImpl(const Slice& target) {
TEST_SYNC_POINT("IndexBlockIter::Seek:0");
PERF_TIMER_GUARD(block_seek_nanos);
if (data_ == nullptr) { // Not init yet
return;
}
Slice seek_key = target;
if (raw_key_.IsUserKey()) {
seek_key = ExtractUserKey(target);
}
status_ = Status::OK();
uint32_t index = 0;
bool skip_linear_scan = false;
bool ok = false;
if (prefix_index_) {
bool prefix_may_exist = true;
ok = PrefixSeek(target, &index, &prefix_may_exist);
if (!prefix_may_exist) {
// This is to let the caller to distinguish between non-existing prefix,
// and when key is larger than the last key, which both set Valid() to
// false.
current_ = restarts_;
status_ = Status::NotFound();
}
// restart interval must be one when hash search is enabled so the binary
// search simply lands at the right place.
skip_linear_scan = true;
} else if (value_delta_encoded_) {
ok = BinarySeek<DecodeKeyV4>(seek_key, &index, &skip_linear_scan);
} else {
ok = BinarySeek<DecodeKey>(seek_key, &index, &skip_linear_scan);
}
if (!ok) {
return;
}
FindKeyAfterBinarySeek(seek_key, index, skip_linear_scan);
}
- 初始化data block iterator
void BlockBasedTableIterator::InitDataBlock() {
BlockHandle data_block_handle = index_iter_->value().handle;
if (!block_iter_points_to_real_block_ ||
data_block_handle.offset() != prev_block_offset_ ||
// if previous attempt of reading the block missed cache, try again
block_iter_.status().IsIncomplete()) {
if (block_iter_points_to_real_block_) {
ResetDataIter();
}
auto* rep = table_->get_rep();
bool is_for_compaction =
lookup_context_.caller == TableReaderCaller::kCompaction;
// Prefetch additional data for range scans (iterators).
// Implicit auto readahead:
// Enabled after 2 sequential IOs when ReadOptions.readahead_size == 0.
// Explicit user requested readahead:
// Enabled from the very first IO when ReadOptions.readahead_size is set.
block_prefetcher_.PrefetchIfNeeded(
rep, data_block_handle, read_options_.readahead_size, is_for_compaction,
/*no_sequential_checking=*/false, read_options_.rate_limiter_priority);
Status s;
table_->NewDataBlockIterator<DataBlockIter>(
read_options_, data_block_handle, &block_iter_, BlockType::kData,
/*get_context=*/nullptr, &lookup_context_,
block_prefetcher_.prefetch_buffer(),
/*for_compaction=*/is_for_compaction, /*async_read=*/false, s);
block_iter_points_to_real_block_ = true;
CheckDataBlockWithinUpperBound();
}
}
在NewDataBlockIterator里面会读取SST文件进行解压缩,并保存到block cache中。
// Convert an index iterator value (i.e., an encoded BlockHandle)
// into an iterator over the contents of the corresponding block.
// If input_iter is null, new a iterator
// If input_iter is not null, update this iter and return it
template <typename TBlockIter>
TBlockIter* BlockBasedTable::NewDataBlockIterator(
const ReadOptions& ro, const BlockHandle& handle, TBlockIter* input_iter,
BlockType block_type, GetContext* get_context,
BlockCacheLookupContext* lookup_context,
FilePrefetchBuffer* prefetch_buffer, bool for_compaction, bool async_read,
Status& s) const {
PERF_TIMER_GUARD(new_table_block_iter_nanos);
TBlockIter* iter = input_iter != nullptr ? input_iter : new TBlockIter;
if (!s.ok()) {
iter->Invalidate(s);
return iter;
}
CachableEntry<Block> block;
if (rep_->uncompression_dict_reader && block_type == BlockType::kData) {
CachableEntry<UncompressionDict> uncompression_dict;
const bool no_io = (ro.read_tier == kBlockCacheTier);
s = rep_->uncompression_dict_reader->GetOrReadUncompressionDictionary(
prefetch_buffer, no_io, ro.verify_checksums, get_context,
lookup_context, &uncompression_dict);
if (!s.ok()) {
iter->Invalidate(s);
return iter;
}
const UncompressionDict& dict = uncompression_dict.GetValue()
? *uncompression_dict.GetValue()
: UncompressionDict::GetEmptyDict();
s = RetrieveBlock(prefetch_buffer, ro, handle, dict, &block, block_type,
get_context, lookup_context, for_compaction,
/* use_cache */ true, /* wait_for_cache */ true,
async_read);
} else {
s = RetrieveBlock(
prefetch_buffer, ro, handle, UncompressionDict::GetEmptyDict(), &block,
block_type, get_context, lookup_context, for_compaction,
/* use_cache */ true, /* wait_for_cache */ true, async_read);
}
if (s.IsTryAgain() && async_read) {
return iter;
}
if (!s.ok()) {
assert(block.IsEmpty());
iter->Invalidate(s);
return iter;
}
assert(block.GetValue() != nullptr);
// Block contents are pinned and it is still pinned after the iterator
// is destroyed as long as cleanup functions are moved to another object,
// when:
// 1. block cache handle is set to be released in cleanup function, or
// 2. it's pointing to immortal source. If own_bytes is true then we are
// not reading data from the original source, whether immortal or not.
// Otherwise, the block is pinned iff the source is immortal.
const bool block_contents_pinned =
block.IsCached() ||
(!block.GetValue()->own_bytes() && rep_->immortal_table);
iter = InitBlockIterator<TBlockIter>(rep_, block.GetValue(), block_type, iter,
block_contents_pinned);
if (!block.IsCached()) {
if (!ro.fill_cache) {
Cache* const block_cache = rep_->table_options.block_cache.get();
if (block_cache) {
// insert a dummy record to block cache to track the memory usage
Cache::Handle* cache_handle = nullptr;
CacheKey key = CacheKey::CreateUniqueForCacheLifetime(block_cache);
s = block_cache->Insert(key.AsSlice(), nullptr,
block.GetValue()->ApproximateMemoryUsage(),
nullptr, &cache_handle);
if (s.ok()) {
assert(cache_handle != nullptr);
iter->RegisterCleanup(&ForceReleaseCachedEntry, block_cache,
cache_handle);
}
}
}
} else {
iter->SetCacheHandle(block.GetCacheHandle());
}
block.TransferTo(iter);
return iter;
}
- 读取data block,里面也会对data block进行二分查找
void DataBlockIter::SeekImpl(const Slice& target) {
Slice seek_key = target;
PERF_TIMER_GUARD(block_seek_nanos);
if (data_ == nullptr) { // Not init yet
return;
}
uint32_t index = 0;
bool skip_linear_scan = false;
bool ok = BinarySeek<DecodeKey>(seek_key, &index, &skip_linear_scan);
if (!ok) {
return;
}
FindKeyAfterBinarySeek(seek_key, index, skip_linear_scan);
}
最终在FindKeyAfterBinarySeek中将解析好的key/value设置好并返回
Next
Next部分就非常简单,调用DataBlock的Next即可,在DataBlockIter::NextImpl()里面会将下一个合法key/value设置好并返回。
void BlockBasedTableIterator::Next() {
if (is_at_first_key_from_index_ && !MaterializeCurrentBlock()) {
return;
}
assert(block_iter_points_to_real_block_);
block_iter_.Next();
FindKeyForward();
CheckOutOfBound();
}
到这BlockBasedTableIterator的主干代码就分析完了,这里会再展开解释一下,BlockBasedTableIterator是如何在一个Block之内进行二分查找的。
SST Format
首先一个SST文件的格式如下:
- Data Block用来保存真正的数据,而Index Block是Data Block的索引,用来加速查找Data Block
- Meta Block主要保存几类信息:
- Filter
- Index
- Compression Dictionary
- Range deletion tombstone
- MetaIndex Blocks是Meta Block的索引,保存了不同Meta Block的偏移量
- Footer保存Index Block和MetaIndex Block的偏移量,一个Magic Number,以及一些校验信息
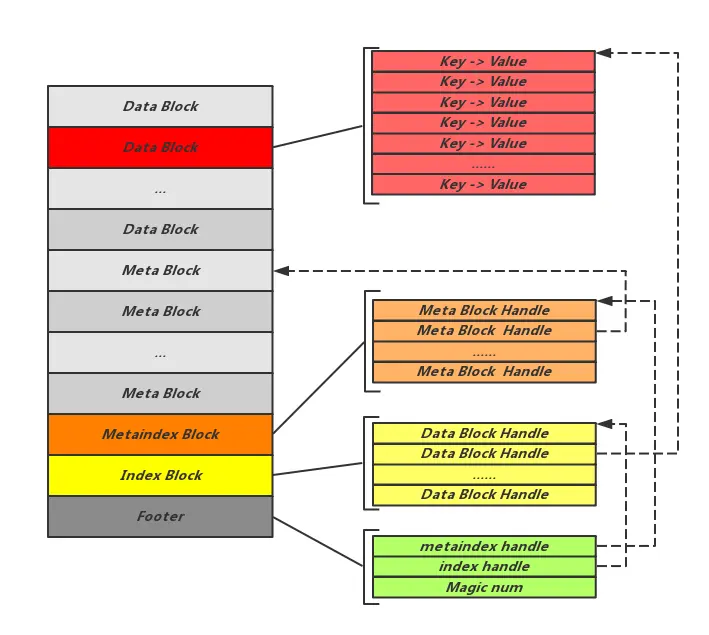
文字形式是这样的:
<beginning_of_file>
[data block 1]
[data block 2]
...
[data block N]
[meta block 1: filter block] (see section: "filter" Meta Block)
[meta block 2: index block]
[meta block 3: compression dictionary block] (see section: "compression dictionary" Meta Block)
[meta block 4: range deletion block] (see section: "range deletion" Meta Block)
[meta block 5: stats block] (see section: "properties" Meta Block)
...
[meta block K: future extended block] (we may add more meta blocks in the future)
[metaindex block]
[Footer] (fixed size; starts at file_size - sizeof(Footer))
<end_of_file>
所以拿到一个SST文件,通过解析Footer,可以获知MetaIndex的偏移量,进而就可以解析到剩余所有Block的偏移量位置。
Block Format
不论是index block还是data block,其物理结构和格式都是相同的。RocksDB的配置中block_size就是每个Block的大小,默认为4K。但其大小只是不是硬限制,即如果新增完一个kv之后,如果大小超过了4K,就会新建一个Block。因此如果单个kv的value非常大,那么对应的Block大小也会非常大,对单个kv不会进行切分。
一个Block的格式如下所示:
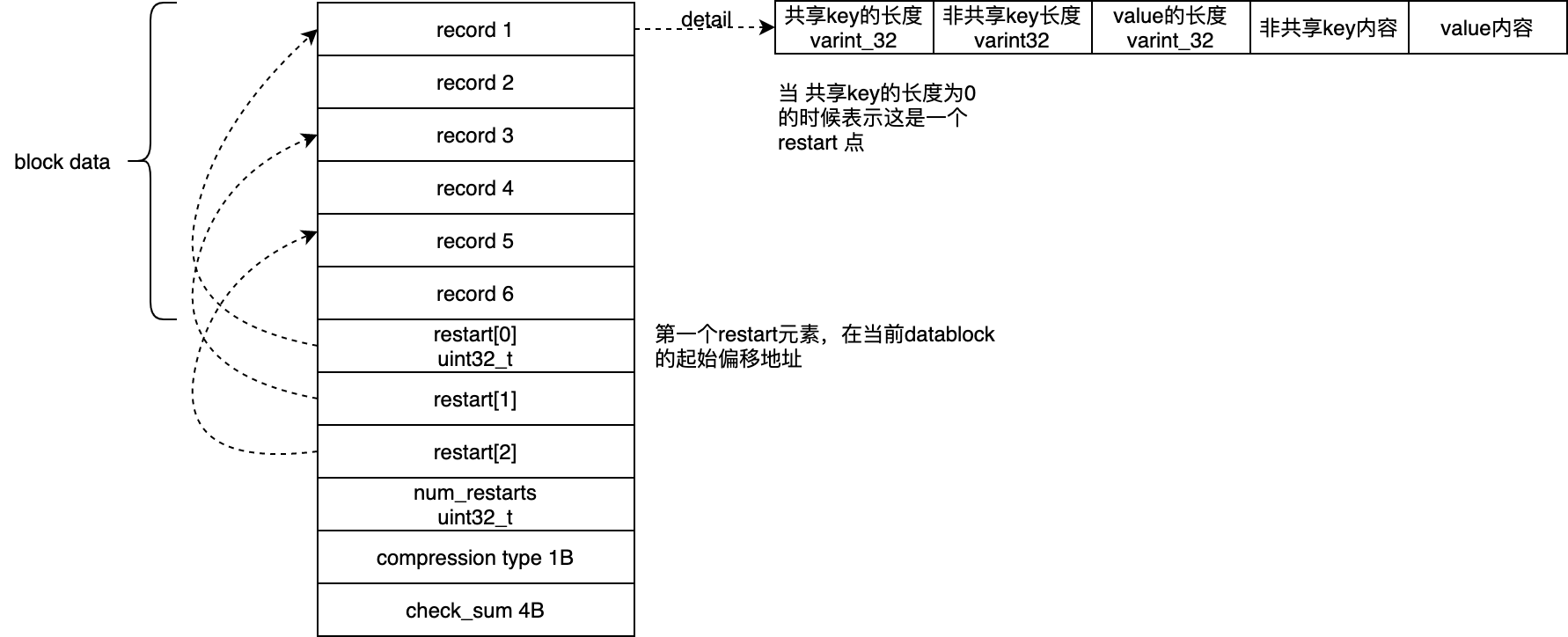
Record用来保存kv数据,一个Record中只保存key-value。由于SST中所有key都是有序存储,因此可以利用delta encoding来节省存储空间。即一个key可以只保存和上一个key不同的部分,而相同的部分只需要记录一个长度即可。另外,Block每隔restart_interval条数据(默认值为16)才完整保存一次key,这些完整保存的key称为restart point。
restart point主要就是为了在单个Block之内进行加速查找,这里有两方面因素:
- 多个restart point也是有序的,因此可以组成一个小型的索引,可以先对restart point进行二分查找,然后再顺序查找
- 由于record中保存了key和value,而restart point只保存key,因此locality会更好
restart point实际在Block中是以偏移量的形式保存的,类型为uint32_t。一个Block的最后保存了有多少个restart point,压缩类型以及校验和。
Binary search in Block
现在可以分析RocksDB是如何在一个Block中进行二分查找。其原理就是首先根据restart point进行二分查找,然后再根据restart point跳转到对应的record开始顺序查找。实现就是非常典型的二分实现,在退出BinarySeek时能保证RestartPoint[index] ≤ target< RestartPoint[index + 1],而skip_linear_scan如果为true,就说明RestartPoint[index] = target,不需要再进行顺序查找。
// Binary searches in restart array to find the starting restart point for the
// linear scan, and stores it in `*index`. Assumes restart array does not
// contain duplicate keys. It is guaranteed that the restart key at `*index + 1`
// is strictly greater than `target` or does not exist (this can be used to
// elide a comparison when linear scan reaches all the way to the next restart
// key). Furthermore, `*skip_linear_scan` is set to indicate whether the
// `*index`th restart key is the final result so that key does not need to be
// compared again later.
template <class TValue>
template <typename DecodeKeyFunc>
bool BlockIter<TValue>::BinarySeek(const Slice& target, uint32_t* index,
bool* skip_linear_scan) {
if (restarts_ == 0) {
// SST files dedicated to range tombstones are written with index blocks
// that have no keys while also having `num_restarts_ == 1`. This would
// cause a problem for `BinarySeek()` as it'd try to access the first key
// which does not exist. We identify such blocks by the offset at which
// their restarts are stored, and return false to prevent any attempted
// key accesses.
return false;
}
*skip_linear_scan = false;
// Loop invariants:
// - Restart key at index `left` is less than or equal to the target key. The
// sentinel index `-1` is considered to have a key that is less than all
// keys.
// - Any restart keys after index `right` are strictly greater than the target
// key.
int64_t left = -1, right = num_restarts_ - 1;
while (left != right) {
// The `mid` is computed by rounding up so it lands in (`left`, `right`].
int64_t mid = left + (right - left + 1) / 2;
uint32_t region_offset = GetRestartPoint(static_cast<uint32_t>(mid));
uint32_t shared, non_shared;
const char* key_ptr = DecodeKeyFunc()(
data_ + region_offset, data_ + restarts_, &shared, &non_shared);
if (key_ptr == nullptr || (shared != 0)) {
CorruptionError();
return false;
}
Slice mid_key(key_ptr, non_shared);
raw_key_.SetKey(mid_key, false /* copy */);
int cmp = CompareCurrentKey(target);
if (cmp < 0) {
// Key at "mid" is smaller than "target". Therefore all
// blocks before "mid" are uninteresting.
left = mid;
} else if (cmp > 0) {
// Key at "mid" is >= "target". Therefore all blocks at or
// after "mid" are uninteresting.
right = mid - 1;
} else {
// target和mid指向的restart point相同 就不需要后续顺序查找了
*skip_linear_scan = true;
left = right = mid;
}
}
if (left == -1) {
// All keys in the block were strictly greater than `target`. So the very
// first key in the block is the final seek result.
*skip_linear_scan = true;
*index = 0;
} else {
*index = static_cast<uint32_t>(left);
}
return true;
}
如果已经找到了合适的restart point,接下来就可以开始顺序查找了。max_offset是这次顺序查找的最大偏移量,如果超过max_offset还没有找到就可以退出循环了。
template <class TValue>
void BlockIter<TValue>::FindKeyAfterBinarySeek(const Slice& target,
uint32_t index,
bool skip_linear_scan) {
// SeekToRestartPoint() only does the lookup in the restart block. We need
// to follow it up with NextImpl() to position the iterator at the restart
// key.
SeekToRestartPoint(index);
NextImpl();
if (!skip_linear_scan) {
// Linear search (within restart block) for first key >= target
uint32_t max_offset;
if (index + 1 < num_restarts_) {
// We are in a non-last restart interval. Since `BinarySeek()` guarantees
// the next restart key is strictly greater than `target`, we can
// terminate upon reaching it without any additional key comparison.
max_offset = GetRestartPoint(index + 1);
} else {
// We are in the last restart interval. The while-loop will terminate by
// `Valid()` returning false upon advancing past the block's last key.
max_offset = std::numeric_limits<uint32_t>::max();
}
while (true) {
NextImpl();
if (!Valid()) {
break;
}
if (current_ == max_offset) {
assert(CompareCurrentKey(target) > 0);
break;
} else if (CompareCurrentKey(target) >= 0) {
break;
}
}
}
}
Reference
RocksDB block-based SST 文件详解 - 简书 (jianshu.com)
Rocksdb Compaction 源码详解(一):SST文件详细格式源码解析_rocksdb sst 文件压缩-CSDN博客